Please Choose Your Language
Please Choose Your Language
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
MH-OSB
MINGHUNG
1. Core Definition and Final Product
Production Line Definition: A complete set of equipment that automatically and continuously processes small-diameter logs (e.g., pine, poplar) or wood residues into multi-layer oriented strand boards through a series of dedicated machinery and processes.
Final Product — OSB Board: An engineered wood panel created by mimicking the natural structure of wood. Its core principle lies in the layered, oriented forming of elongated wood strands (typically with surface layers oriented longitudinally and the core layer oriented crosswise), followed by hot-pressing. This gives it exceptional bending strength, dimensional stability, and nail-holding power, earning it the title "king of structural panels." It is widely used in building structures (walls, flooring, roofing), packaging, and furniture substrates.
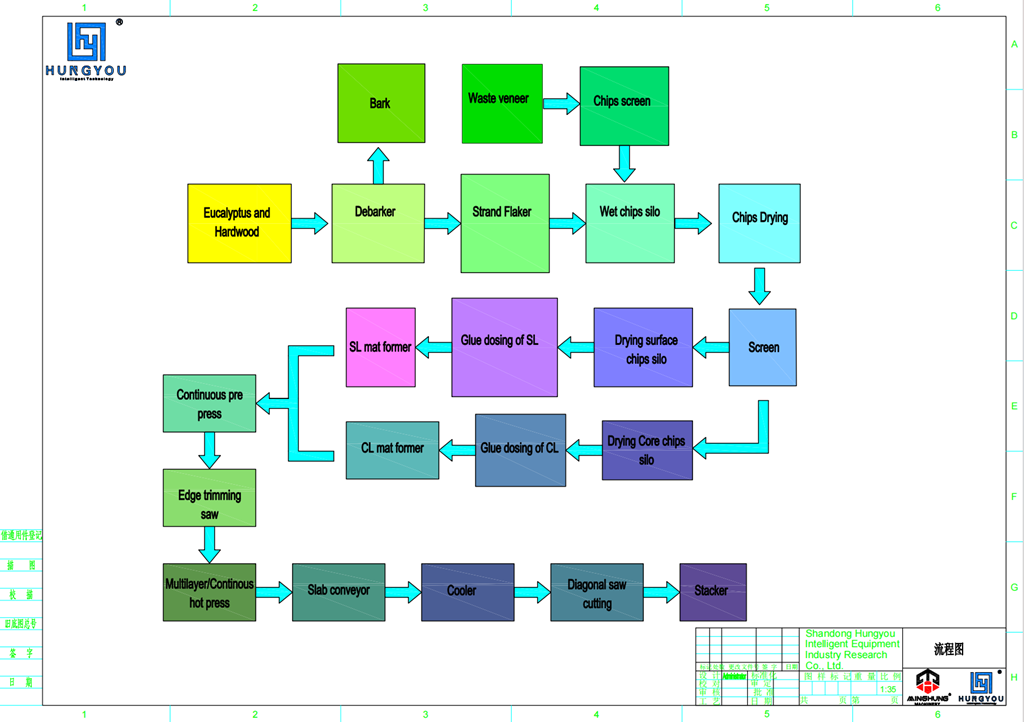
Production line process
The process flow of a Multi-Layer Oriented Strand Board (OSB) Production Line is a fully automated, continuous, and integrated system. Its core objective is to achieve the oriented layup of wood strands, thereby imparting superior structural properties to the final panels. The entire process begins with raw log material and concludes with finished OSB boards, all coordinated and controlled by a central intelligent control system.
The specific process steps are as follows:
1. Strand Preparation Section: Logs or wood raw material first enter this section. Through flakers and stranders, the wood is processed into standard-sized, long, thin wood strands, which are the fundamental units that constitute the board's mechanical properties.
2. Drying and Screening Section: The prepared strands are conveyed into the drying system (typically an efficient triple-pass rotary drum dryer), where their moisture content is drastically reduced from a high 40%-60% to a hot-pressing suitable 2%-4%. Screening occurs both before and after drying to remove fines and dust, ensuring only dimensionally qualified, clean strands proceed.
3. Blending and Additives Section: The qualified strands enter the core equipment—the ring blender. Here, the strands are uniformly coated with atomized resin (e.g., MDI, phenolic resin) and liquid wax for waterproofing, preparing them for bonding during hot-pressing.
4. Forming and Mat Forming Section (The Core): This is the critical stage where the board's "oriented structure" is created. The resinated strands are laid and oriented by a precision mechanical or pneumatic forming head to form a mat. The classic "sandwich" structure is achieved by having face-layer strands oriented longitudinally (along the production line direction) and core-layer strands oriented crosswise, creating a stable, multi-layer, cross-oriented mat.
5. Pressing and Finishing Section: The formed mat enters a continuous flat press, where it is cured under precisely controlled high temperature and pressure to form a continuous board. This board then undergoes cooling, trimming/cutting to specified dimensions, and finally surface sanding, resulting in finished OSB boards with uniform thickness and a smooth surface.
Main Production Line Sections
1. Strand Preparation Section
Flakers/Stranders: Process logs or wood blocks into standard-sized, long, thin strands—the "foundational material" that determines the board's mechanical properties.
Re-crusher & Screening System: Breaks down oversized strands and screens for qualified strands, removing fines and dust to ensure mat forming quality.
2. Drying & Screening Section
Rotary Drum Dryer: Typically employs efficient, energy-saving triple-pass drum dryers to reduce strand moisture content from 40%-60% to 2%-4%, meeting hot-pressing requirements.
Vibratory Screening: Fine screening after drying to ensure optimal strand size for face and core layers.
3. Blending & Additives Section
Ring Blender: The core equipment. Strands are evenly coated with atomized resin (commonly PMDI/MDI or phenolic resin) inside the high-speed rotating blender.
Wax Application System: Simultaneously adds liquid wax to enhance the board's moisture and water resistance.
4. Forming & Mat Forming Section (Technological Core)
Mechanical/Pneumatic Forming Machine: This is the "heart" of the line. Through precision mechanical arms or airflow guidance devices, surface strands are oriented in the production line direction (longitudinal), while core strands are oriented crosswise, creating a stable "three-layer (or multi-layer) cross-oriented structure." Forming accuracy directly determines the board's mechanical properties.
5. Pressing & Finishing Section
Continuous Flat Press: The hallmark of a modern line. The formed mat is simultaneously heated and pressed in a long, continuously running hot press, enabling continuous, stable, and highly efficient production with excellent uniformity and quality.
Cooling, Flipping, Sawing, Sanding Systems: Cools the continuous pressed board, cuts it to size via cross-cut and trim saws, and sands the surface to ensure precise thickness tolerance and smoothness.
6. Central Intelligent Control System
 An integrated PLC/DCS control system that enables automatic control and interlocking of speed, temperature, pressure, flow, and ratios across the entire line, ensuring process stability. This is key to the high efficiency, low consumption, and reduced labor requirements of modern lines.
An integrated PLC/DCS control system that enables automatic control and interlocking of speed, temperature, pressure, flow, and ratios across the entire line, ensuring process stability. This is key to the high efficiency, low consumption, and reduced labor requirements of modern lines.
Key Technical Parameters & Configuration Options
Capacity: Typically measured in annual output, ranging from 30,000 cubic meters (entry-level line) to over 300,000 cubic meters (large continuous press line).
Product Specifications:
Thickness Range: Usually 6mm ~ 40mm, adjustable.
Panel Size: Standard is 1220mm × 2440mm (4'×8'), larger sizes customizable based on press width.
Density: Approximately 600 - 680 kg/m³.
Configuration Options:
Resin Type: Can be adapted for eco-friendly MDI resin (no formaldehyde added) to produce ENF grade or no-added-formaldehyde boards.
Energy Solution: Can utilize various heat sources like natural gas, biomass fuel, steam, or thermal oil.
Automation Level: Ranges from basic automation to fully automated "lights-out factory" solutions equipped with AGVs, robotic stacking, and smart warehousing systems.
We provide comprehensive turnkey project services, including plant planning, equipment installation & commissioning, and operator training, to help clients rapidly establish a competitive edge in the fast-growing engineered wood panel market.
Our contacts:
Whatsapp: +8618769900191 +8615589105786 +8618954906501
Email: osbmdfmachinery@gmail.com
1. Core Definition and Final Product
Production Line Definition: A complete set of equipment that automatically and continuously processes small-diameter logs (e.g., pine, poplar) or wood residues into multi-layer oriented strand boards through a series of dedicated machinery and processes.
Final Product — OSB Board: An engineered wood panel created by mimicking the natural structure of wood. Its core principle lies in the layered, oriented forming of elongated wood strands (typically with surface layers oriented longitudinally and the core layer oriented crosswise), followed by hot-pressing. This gives it exceptional bending strength, dimensional stability, and nail-holding power, earning it the title "king of structural panels." It is widely used in building structures (walls, flooring, roofing), packaging, and furniture substrates.
Production line process
The process flow of a Multi-Layer Oriented Strand Board (OSB) Production Line is a fully automated, continuous, and integrated system. Its core objective is to achieve the oriented layup of wood strands, thereby imparting superior structural properties to the final panels. The entire process begins with raw log material and concludes with finished OSB boards, all coordinated and controlled by a central intelligent control system.
The specific process steps are as follows:
1. Strand Preparation Section: Logs or wood raw material first enter this section. Through flakers and stranders, the wood is processed into standard-sized, long, thin wood strands, which are the fundamental units that constitute the board's mechanical properties.
2. Drying and Screening Section: The prepared strands are conveyed into the drying system (typically an efficient triple-pass rotary drum dryer), where their moisture content is drastically reduced from a high 40%-60% to a hot-pressing suitable 2%-4%. Screening occurs both before and after drying to remove fines and dust, ensuring only dimensionally qualified, clean strands proceed.
3. Blending and Additives Section: The qualified strands enter the core equipment—the ring blender. Here, the strands are uniformly coated with atomized resin (e.g., MDI, phenolic resin) and liquid wax for waterproofing, preparing them for bonding during hot-pressing.
4. Forming and Mat Forming Section (The Core): This is the critical stage where the board's "oriented structure" is created. The resinated strands are laid and oriented by a precision mechanical or pneumatic forming head to form a mat. The classic "sandwich" structure is achieved by having face-layer strands oriented longitudinally (along the production line direction) and core-layer strands oriented crosswise, creating a stable, multi-layer, cross-oriented mat.
5. Pressing and Finishing Section: The formed mat enters a continuous flat press, where it is cured under precisely controlled high temperature and pressure to form a continuous board. This board then undergoes cooling, trimming/cutting to specified dimensions, and finally surface sanding, resulting in finished OSB boards with uniform thickness and a smooth surface.

Main Production Line Sections
1. Strand Preparation Section
Flakers/Stranders: Process logs or wood blocks into standard-sized, long, thin strands—the "foundational material" that determines the board's mechanical properties.
Re-crusher & Screening System: Breaks down oversized strands and screens for qualified strands, removing fines and dust to ensure mat forming quality.
2. Drying & Screening Section
Rotary Drum Dryer: Typically employs efficient, energy-saving triple-pass drum dryers to reduce strand moisture content from 40%-60% to 2%-4%, meeting hot-pressing requirements.
Vibratory Screening: Fine screening after drying to ensure optimal strand size for face and core layers.
3. Blending & Additives Section
Ring Blender: The core equipment. Strands are evenly coated with atomized resin (commonly PMDI/MDI or phenolic resin) inside the high-speed rotating blender.
Wax Application System: Simultaneously adds liquid wax to enhance the board's moisture and water resistance.
4. Forming & Mat Forming Section (Technological Core)
Mechanical/Pneumatic Forming Machine: This is the "heart" of the line. Through precision mechanical arms or airflow guidance devices, surface strands are oriented in the production line direction (longitudinal), while core strands are oriented crosswise, creating a stable "three-layer (or multi-layer) cross-oriented structure." Forming accuracy directly determines the board's mechanical properties.
5. Pressing & Finishing Section
Continuous Flat Press: The hallmark of a modern line. The formed mat is simultaneously heated and pressed in a long, continuously running hot press, enabling continuous, stable, and highly efficient production with excellent uniformity and quality.
Cooling, Flipping, Sawing, Sanding Systems: Cools the continuous pressed board, cuts it to size via cross-cut and trim saws, and sands the surface to ensure precise thickness tolerance and smoothness.
6. Central Intelligent Control System
 An integrated PLC/DCS control system that enables automatic control and interlocking of speed, temperature, pressure, flow, and ratios across the entire line, ensuring process stability. This is key to the high efficiency, low consumption, and reduced labor requirements of modern lines.
An integrated PLC/DCS control system that enables automatic control and interlocking of speed, temperature, pressure, flow, and ratios across the entire line, ensuring process stability. This is key to the high efficiency, low consumption, and reduced labor requirements of modern lines.
Key Technical Parameters & Configuration Options
Capacity: Typically measured in annual output, ranging from 30,000 cubic meters (entry-level line) to over 300,000 cubic meters (large continuous press line).
Product Specifications:
Thickness Range: Usually 6mm ~ 40mm, adjustable.
Panel Size: Standard is 1220mm × 2440mm (4'×8'), larger sizes customizable based on press width.
Density: Approximately 600 - 680 kg/m³.
Configuration Options:
Resin Type: Can be adapted for eco-friendly MDI resin (no formaldehyde added) to produce ENF grade or no-added-formaldehyde boards.
Energy Solution: Can utilize various heat sources like natural gas, biomass fuel, steam, or thermal oil.
Automation Level: Ranges from basic automation to fully automated "lights-out factory" solutions equipped with AGVs, robotic stacking, and smart warehousing systems.
We provide comprehensive turnkey project services, including plant planning, equipment installation & commissioning, and operator training, to help clients rapidly establish a competitive edge in the fast-growing engineered wood panel market.
Our contacts:
Whatsapp: +8618769900191 +8615589105786 +8618954906501
Email: osbmdfmachinery@gmail.com
